Write something in the search field

Your needs, our challenges
Thermography is a technique that allows to determine temperatures at a distance and without the need for physical contact with the object to be studied, allowing the capture of infrared radiation of the electromagnetic spectrum. Knowing the data on the environmental conditions —air humidity and temperature, distance to the thermographed object, reflected temperature, incident radiation— and the characteristics of the thermographed surfaces such as emissivity, the radiated energy detected by the thermographic camera can be converted into temperature values. In a thermography, each pixel corresponds to a temperature value in the radiation measurement; This image can be defined as radiometric.
This makes the field of industrial applications of this technique quite wide. The ability to measure the temperature of an object, or a specific position thereof, in real time and without the physical contact of a measuring element, implies advantages when it comes to reducing the instrumentation or sensor network necessary for such effect. Thermography also allows the reduction of the use of wiring as long as we have a wide field of vision of the surface or object to be measured.
In predictive maintenance tasks, this technique has been used for some time to detect “hot spots” in rotating machinery and electrical connections where the current flow is high, detecting in advance possible faults that may affect the optimal performance of the installation.
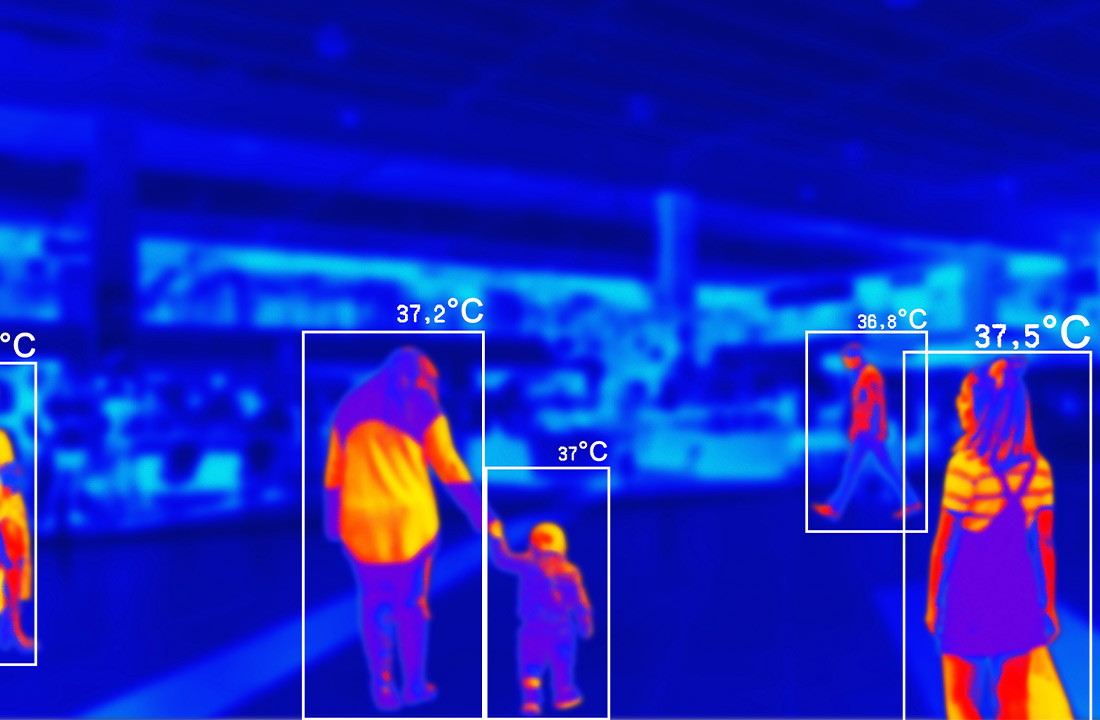
Of special relevance has also been its use in access control systems to large facilities (airports, public transport stations, large companies and corporations, …), allowing the creation of a “thermal map” of the users of said services in real time.
Another clear example of how thermography is not an invasive technique.
With 100 years of experience in providing high quality and reliable products, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation is a recognized world leader in the manufacture, marketing and sale of electrical and electronic equipment, focused on all types of applications: information processing and communications, space development and satellite communications, consumer electronics, industrial technology, energy, transportation, and construction equipment. Through the spirit of “Changes for the Better”, Mitsubishi Electric strives to enrich society with technology.
As a result of their experience, in 2019 they presented us with the MeIDIR sensor, specially designed for space applications, and developed for use in the Advanced Earth Observation Satellite-2 called DAICHI-2 or ALOS-2. The sensor was designed with a high resolution of 80×32 pixels, a field of view of 78°x29°, and a thermal resolution of 100mK for better efficiency in identifying people and objects.
In 2022, Mitsubishi opens the doors to an updated and improved version (MIR8060B1), expanding the current field of view from 78ºx29º to 78°x53°, achieving a higher resolution from 80×32 pixels to 80×60 pixels, so the detection area is 2 to 4 times larger and thermal resolution of 100mK, or 0.1°C, is maintained.
The MelDIR sensor achieves excellent thermal imaging as well as higher resolution at a smaller size and lower cost, making this version more versatile and competitive.
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation expands its range of Mitsubishi Diode Infrared Sensors (MelDIR) by introducing a new thermal sensor with increased field of view (FoV) and high resolution of 80×60 pixels, specially designed for security, heating, ventilation and air conditioning applications ( HVAC), people counting, smart buildings and thermal scanners.
The new MelDIR sensor [MIR8060B1] accurately distinguishes all heat sources and allows the identification of specific human behaviors, such as walking, running or raising hands.
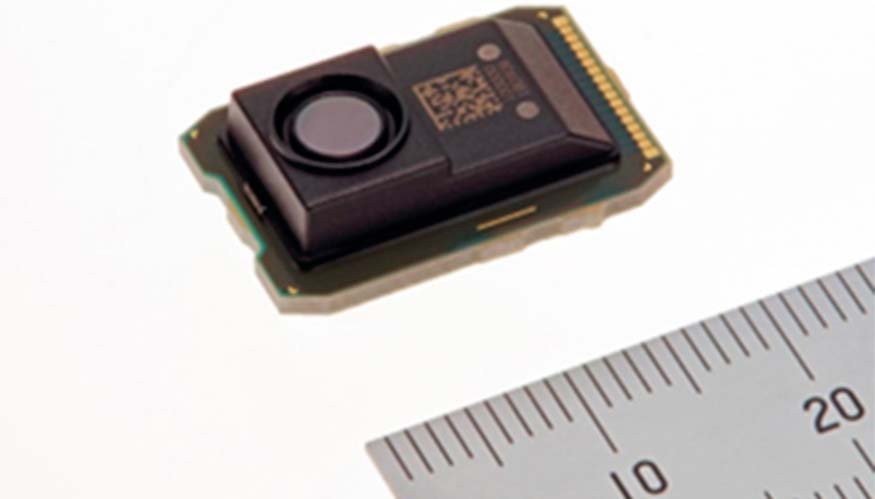
Illustration 1. New MelDIR thermal diode infrared sensor (80 x 60 pixels).
Without changing the size, with this new MIR8060B1 sensor we extend the current field of view from 78ºx29º to 78°x53°, achieving a higher resolution from 80×32 pixels to 80×60 pixels, so the detection area is 2 to 4 times larger and thermal resolution of 100mK, or 0.1°C, is maintained.
Compared to a conventional 80×32 pixel MelDIR, a faster frame rate and optimized sensitivity correction are achieved for higher quality thermal images.
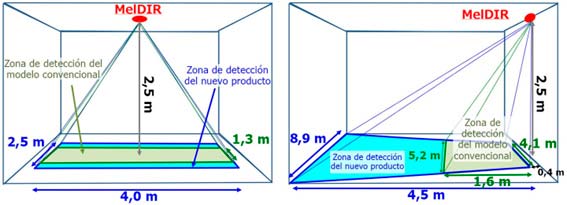
Illustration 2. Comparison between the detection zones of the conventional MelDIR and the new product MIR8060B1.
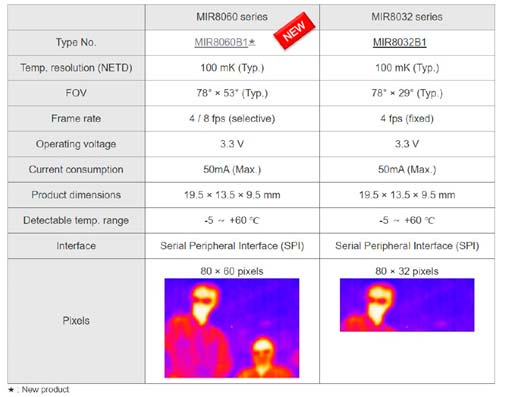
Illustration 3. Comparative range of MelDIR products.
Mitsubishi has a development kit made up of a board that includes a MIR sensor with an interface for USB connection through which the developer can access all the functionalities as well as the configuration parameters necessary for their thermography application.
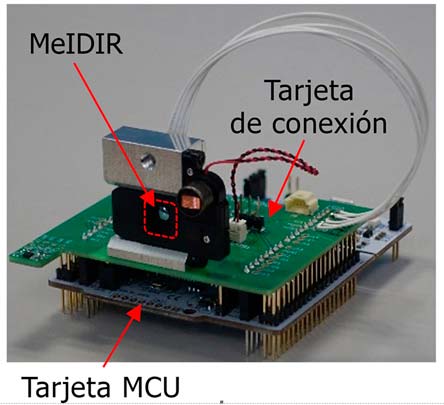
As we have previously reported, this product is indicated for industrial applications where it is sought to reduce the wiring of the thermal sensor network and intrusive presence detection in a security area. In addition, linked to algorithms based on predictive models of thermal evolution, MIR sensors are the perfect tool for monitoring critical areas of power conversion equipment, where the connection points are likely to evolve catastrophically.
At Inelec we are available to our clients to provide technical support in industrial developments based on the new range of Mitsubishi MeIDIR products. Please get in touch via email info@inelec.net
